Fifth Generation Fixed Network (F5G)
Posted by Sabine Dahmen-Lhuissier 64526 HitsIntroduction
We are entering a new era of communication, where fixed networks will play an even more essential role. Fixed networks have always offered the highest bandwidths and availability with the lowest energy usage. The development of a full fibre and full optical solutions will help to support the most demanding applications, such as ultra-high definition video streaming, telemedicine, virtual reality (VR) gaming, and more to come.
Next generations of fixed networks are needed to complement the mobile/ wireless networks (5G/6G) and support the growing number of cloud services requiring high bandwidth and/or low latency connections. Built on previous generations of fixed networks, the ETSI Industry Specification Group (ISG) F5G studies and develops the generations of the fixed network fostering the evolution to a “fibre to everywhere” ecosystem that enables new and enhanced services leveraging, in a framework of growing network capabilities, better performance, intelligent E2E management, network security and enhanced energy efficiency.
ISG F5G aims to work as a hub for the development of fibre-based networks standardization in an E2E perspective, identifying major use cases and requirements and interacting with all relevant SDOs and industry stakeholders to produce new standards, where required, or enhancements to existing standards that may be needed to fulfil the identified use cases.
ETSI ISG F5G developed F5G release 1 and release 2 of the technical specifications addressing the 5th fixed generation standardization. During the next years, ETSI ISG F5G will study and develop the future fixed networks generations, starting from F5G-A (5th generation Advanced) and F6G (6th generation), while maintaining and enhancing the releases already published.
Evolution to F5G Advanced
ETSI ISG F5G will enhance and expand previous solutions to F5G Advanced, and the evolved and new characteristics of the F5G-Advanced network will address six main features:
Enhancement to:Enhanced fixed broadband (eFBB)Guaranteed reliable experience (GRE)
Full-fibre connecti (FFC)Expansion to:
Green Agile Optical-Network (GAO) Real-time Resilient Link (RRL) Optical Sensing and Visualization (OSV)They can be used to represent the evolution of the technology and services (see figure below).
F5G-Advanced will provide over 10 times higher bandwidth, 10 times denser fibre connections, and 10 times better reliability, 10x better energy efficiency, sensing on 1m accuracy, <1 ms latency, autonomous level 4.
F5G-Advanced will open new opportunities by comprehensively applying fibre and optical technology to various scenarios and expanding the reach of fibre to everything, everywhere, to benefit all industry verticals (e.g. telecom, education, healthcare, finance, energy, transportation and manufacturing).
Our Role & Activities
ETSI ISG F5G will study the following aspects:
Identifying and developing the overall characteristics of the F5G-A and the F6G generations of fixed network exploring all relevant F5G-A and F6G scenarios and related use cases and services including (but not limited to) home, business, multiple vertical industries and mobile/ wireless x-haul performing a gap analysis to identify the necessity for both enhancements to existing technology specifications and/or developments of new technology specifications where required to fulfil the identified use cases studying the overall framework, outlining the complete F5G-A and F6G technology landscape developing an E2E reference architecture for F5G-A and F6G networks specifying flexible and agile E2E management, enhancing QoE and QoS managing the ISG F5G Proof of Concept framework leveraging PoC activities that validate specifications, services or architecture options developed throughout the work on ISG F5G evaluating and analysing security aspects of F5G-A (cooperation with TC Cyber) leveraging the synergies between fixed networks (Transport, Aggregation, Access) and wireless communications to foster convergence in residential, enterprise and vertical services studying migration path scenarios towards the F5G-A and the F6GThe expected evolution of the fixed network creates new opportunities by extending the use of optical networks and services to a wide variety of scenarios (home, office, campus, industry and extended support to wireless networks) and increasing their penetration in different environments (Fibre To The Room, Fibre To The Desk, Fibre To The Machine).
Expanding the network capabilities will allow the improvement of existing, and the support of new, services.
The new network capabilities and the new services will include:
Home scenarios where emerging UHD immersive experience and cloud oriented services such as Metaverse, Cloud VR (virtual reality) and AR (augmented reality) video streaming, online gaming, etc., introduce the necessity for ultra-broadband, extremely low latency and zero packet loss. Business scenarios such as enterprise digitization and Cloudification, where premium computing integrated networks enable operators to offer new capabilities and resources in a “X as a service” model, requiring enhanced network capabilities, high reliability and high security. Vertical industry scenarios with stringent demand for deterministic networking, very low latency and packet jitter, high reliability, network slicing for addressing different business needs, digital twins and requirements for end to end computing power and networking coordination. The massive deployment of wireless networks, primarily in 5G and beyond, bringing growing needs for an efficient optical infrastructure that can deliver the bandwidth, latency and dense distribution required to support those networks. The green and digital transformation, requiring the improving energy efficiency that optical networks can offer (cooperation with TC EE). The evolution towards the autonomous network paradigm. The enablement of services based on the sensing capabilities of fibre cables and Wi-Fi, both for enhancements of the network management as well as new service offerings that make use of those capabilitiesIndustry use cases and relevant potential requirements will be clearly documented with the corresponding technology landscape.
F5G full fibre approach aims to maximize the synergy with the related transport, access and in-premises technologies such as fgOTN, 50G-PON and supplementary technologies such as Wi-Fi 7 and FTTR. New technologies or extensions to existing technologies will be identified through gap analyses. These extensions may include:
Digitized ODN Technologies 50G-PON Enhancements Wi-Fi 7 Enhancements Underlay and Service Plane separation Smart energy efficiency End-to-End full stack slicing Autonomous O & M Artificial Intelligence Network synergy Industrial Optical Networks Mobile X-haul Convergence with 5G/6G fgOTN/OTN, OXC/ROADM, 800G WDM Optical Service Networks FTTR/FTTM/FTTO/FTTThingThese new features will be supported by an E2E network architecture looking at same time at the best evolution path.
ETSI ISG F5G considers a wide range of technologies, and therefore seeks to actively cooperate with several relevant standardization groups, both inside and outside of ETSI, as well as vertical industrial organizations. ETSI ISG F5G’s work will be oriented to pre-standardization including the identification of technology and standards gaps. Any areas of interest will be referred to the appropriate standardization group and/or organization which may then further enhance or develop the relevant technology specifications.
Specifications
The group published the F5G Release 1. Description of Release 1.
The group published the F5G Release 2. Description of Release 2.
For F5G Advanced Releases refer to the Open Area containing up-to-date release descriptions.
A full list of related standards in the public domain is accessible via the ETSI F5G committee page.
Blog
News, comments and opinions from ETSI’s F5G Industry Specification GroupThe direct link to refer to this blog is https://www.etsi.org/newsroom/blogs/blog-F5G
ETSI ISG F5G has brought together industry, academia, and research experts to start shaping the vision for F6G: the next generation of fixed optical networks. The workshop included visions and priorities for F6G from different perspectives, use cases, scenarios, and business needs, research and technologies currently in development for F6G, key challenges on the path to F6G.
ETSI F5G ISG publishes its first Test WG Specification – "Test Specification for Residential FTTR Functionality and Performance", a landmark test specification for Fibre-to-the-Room (FTTR) functionality and performance. This crucial document establishes the global test standard for Fibre-to-the-Room (FTTR) systems, ensuring gigabit speeds, seamless roaming, and carrier-grade reliability for next-generation in-home networks. Discover how this specification paves the way for widespread, high-quality FTTR deployment.

AI for in-home networks and their services is a crucial aspect in the F5G Advanced era, as operators need to monetise the network beyond pure connectivity and gain a competitive advantage in providing home broadband connectivity. Organised by ETSI ISG F5G, this session provided various perspectives on use cases and scenarios, technical requirements, network architecture, standardisation progress, and innovation with proof-of-concepts on AI for FTTR/in‑home networks and services.
Green development has become a global consensus key priority to address the climate change, in which ICT plays an important role. In ETSI ISG F5G, Green Agile Optical network (GAO) has been defined as one of the six key characteristics of F5G-A.
In the week of September 15th ~ 18th 2025, the ETSI F5G F2F#23 was held in Chengdu, China, hosted by China Telecom. On 17 September 2025 during the F5G plenary meeting, a workshop on "Green Optical Network" was held. Seven experts from network operators, vendors and academia in the area of optical communication shared their visions, scenarios and technologies to enable a greener optical network.
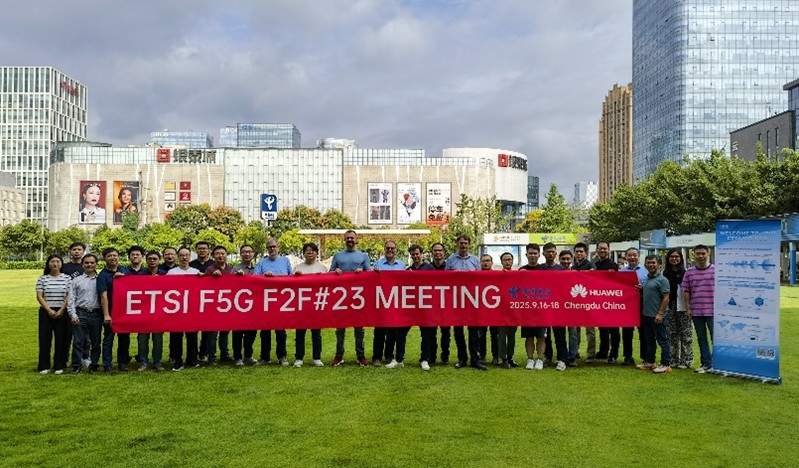

Electricity costs are a major operational expense for telecom operators, making energy efficiency critical. Strategies like optimizing device power consumption and adjusting operational modes can significantly reduce energy use and expenses. In Passive Optical Networks (PONs), traffic volumes fluctuate rapidly, creating periods of low activity. Leveraging this, PON ports can transit to low-power modes during idle periods to conserve energy. Achieving this requires a real-time traffic load sensing system that dynamically adjusts the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) interface mode based on energy-saving scenarios, enabling a closed-loop mechanism for perception, control, and execution. Accurate traffic prediction is essential for effective energy savings. Traditional SNMP polling (15-minute intervals) is too slow for granular traffic forecasting. China Telecom addressed this by pioneering Technical Specifications for Access Network Telemetry, enabling rapid data collection via active reporting protocols (see ETSI GS F5G 011 V1.1.1 (2022‑11) and ETSI GS F5G 016 V1.1.1 (2023‑06). A Proof of Concept and experiments in a region have been performed. There is no customer complaint claimed when energy-saving is enabled, so services are not affected or the impact is small.
In April 2025, ETSI published a new Group Report (GR), ETSI GR F5G 019 (Fifth Generation Fixed Network (F5G); Fixed Network Autonomous Network level definition and evaluation), which was developed in the ETSI ISG F5G.
This document provides an evaluation basis for measuring the Autonomous Network levels (from L0 to L5) of a Fixed Network (including Optical Transport Network and the Access and Residential Networks) along with its components and workflows, and defines the evaluation methodology to score the level of a specific system in a Fixed Network.
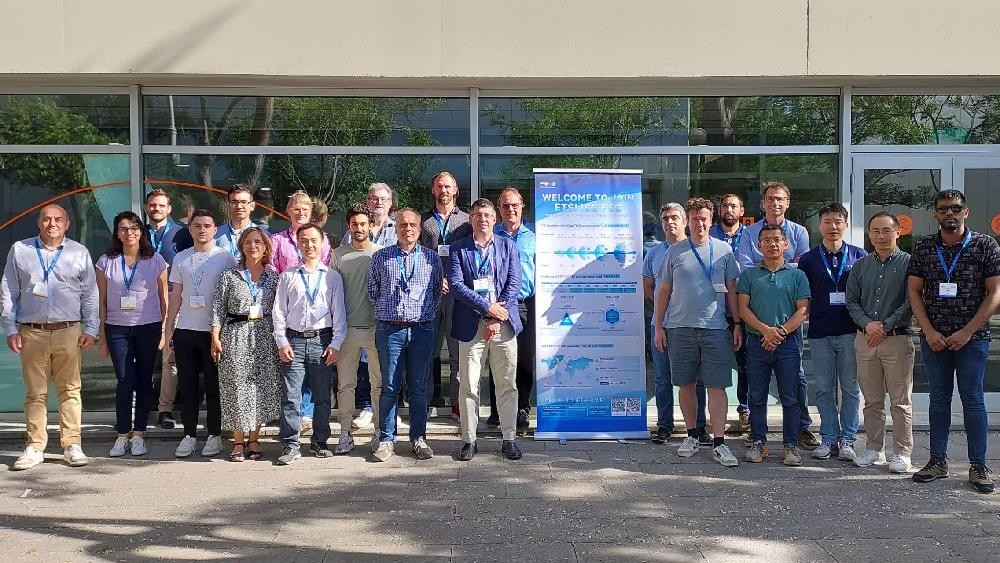
In the week of May 19th ~ 23rd 2025, global industry and academic experts in the area of optical communication gathered in Castelldefels (Barcelona), Spain to discuss F5G-Advanced network architecture and future roadmap to F6G, and identify potential open-source implementation driven by TFS and OSL to develop PoCs of the F5G-Advanced architectures. The groups involved were ETSI SDG OSL (Software Development Group OpenSlice), SDG TFS (Software Development Group TeraFlowSDN) and ISG F5G. CTTC hosted all these meetings in its headquarters.
During this week, an open joint session between SDG OSL, SDG TFS and ISG F5G was held for the first time. The intelligent network management & control and the automatic service provisioning of the F5G Advanced networks, which contain multiple fixed network segments, becomes the common interests of these three groups.

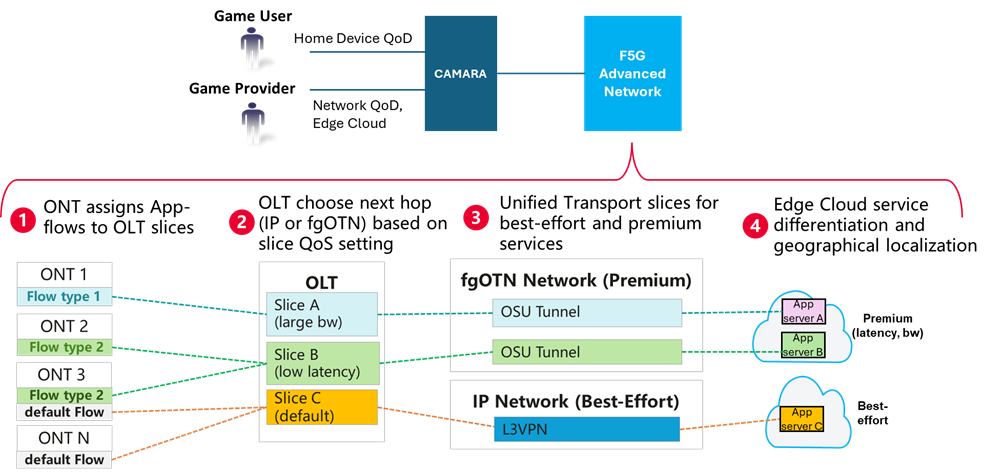
At the Mobile World Congress 2025, the Centre Tecnològic de Telecomunicacions de Catalunya (CTTC) and Huawei Technologies showcased a cutting-edge Proof of Concept (PoC) focused on the development of a standards-based and open-source Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) platform. This initiative aligns with specifications from key standards organizations such as ETSI, IETF, and CAMARA, and is built upon open-source components including ETSI TeraFlowSDN (TFS) and ETSI Open Source MANO (OSM). The proposed solution highlights the capabilities of the ETSI Industrial Specification Group (ISG) Fifth Generation Fixed (F5G) Network. This demonstration introduced a set of technical Fixed 5G technology enhancements focused on end-to-end service delivery and network automation, using an immersive Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality (AR/VR) Gaming Service for Remote Players as a practical application of the F5G Advanced (F5G-A) architecture. The platform demonstrated end-to-end QoD capabilities, incorporating application-flow classification and differentiation. To support this, the setup was expanded to include a dedicated IP transport network for best-effort traffic, operating alongside the fine-grain Optical Transport Network (fgOTN), which was used for traffic requiring guaranteed Quality of Service (QoS). This allowed the system to differentiate between traffic types and manage them accordingly.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) jointly organized the "ITU-ETSI Symposium on ICT Sustainability: Standards Driving Environmental Innovation", held on 11–12 December 2024 at ITU Headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland. It brought together industry leaders, policymakers, researchers and stakeholders to explore the crucial role of standards in promoting sustainable ICT practices. Standards guide the development of technologies that minimize environmental impact and enhance energy efficiency.
The ETSI Industry Specification Group (ISG) on Fifth Generation Fixed Network (F5G) releases the specification titled "Fifth Generation Fixed Network (F5G); Specification for PON based Industrial Network".
Passive Optical Network (PON) is the dominant access network technology for operators all around the world and has been widely deployed in public access networks. It has the advantages of large bandwidth, low deployment cost, uses passive optical distribution network, carrier-grade quality and smart operation and maintenance capabilities.
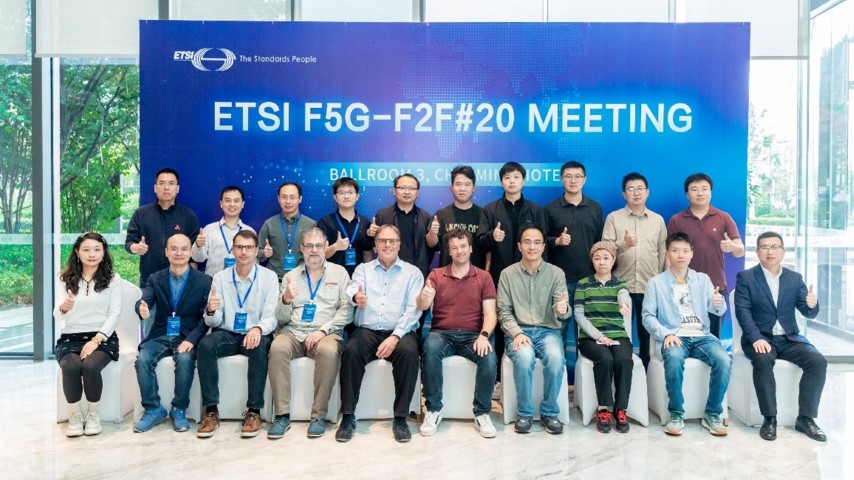
In the week of November 12th to 15th 2024, both the 20th ETSI ISG F5G Plenary meeting and CCSA TC6 WG2 plenary meeting were held, co-located in Jingdezhen, Jiangxi Province, China.
On November 13th 2024 during the two meetings, a workshop on "Evolution of Optical Network Generations: Technologies and Standards" was held. Six experts from both ISG F5G and CCSA TC6 WG2 shared the latest progress of technologies and standards development of optical networks. A panel discussion was held over the topics of future technologies and standard cooperation to promote the next generation of optical networks. The panellists include:
- Dr. Dechao Zhang, CCSA TC6 WG2 Vice Chair, China Mobile
- Dr. Olivier Ferveur, ETSI ISG F5G Chair, POST Luxembourg
- Dr. Jialiang Jin, ETSI ISG F5G Vice Chair, China Telecom
- Mr. Hai Ding, Network innovative product expert from China Unicom
- Ms. Qian Liu, ETSI ISG F5G TEST WG Chair, CAICT
- Dr. Raul Muñoz, Research Director, CTTC
- Dr. Marcus Brunner (Moderator), ETSI ISG F5G Vice Chair, Huawei

Network X 2024 took place from October 8th to 10th at the international conference centre, Paris Expo Porte de Versailles in France. ETSI, a partner of Network X, hosted the "Partner Workshop with ETSI ISG F5G" on the first day of Network X.
This workshop focused on F5G-Advanced initiatives, highlighting the latest developments and progress. It provided the participants with the status norms and the achievement made in F5G-Advanced, which will help to evolve fixed networks.
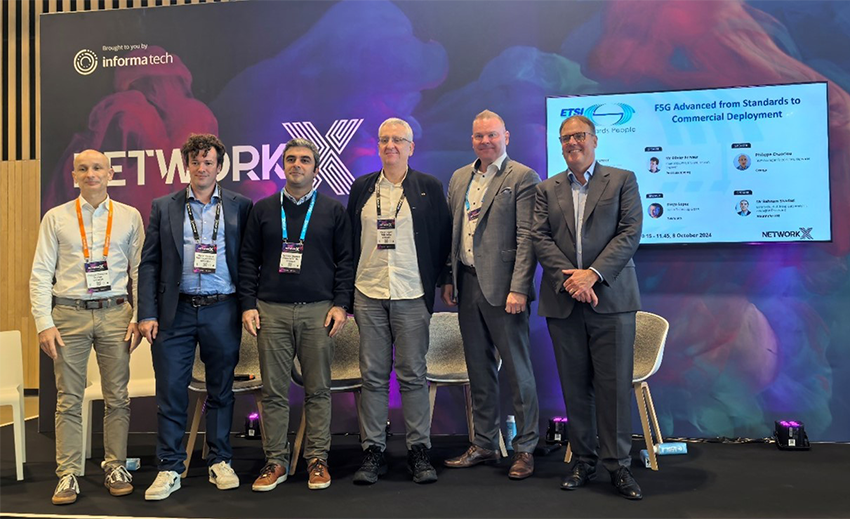

In picture are the five speakers who shared their F5G-Advanced viewpoints, plus the moderator. From left to right we have:
- Dr. Philippe Chanclou, Team Manager of Fixed Access Networks, Orange
- Dr. Olivier Ferveur, ETSI ISG F5G Chair, Post Luxembourg
- Dr. Behnam Shariati, Deputy Head of Group Data Analytics and Signal Processing, Fraunhofer HHI
- Dr. Diego Lopez, ETSI ISG ZSM Chair, Senior Technology Expert, Telefonica
- Mr. Riku Päärni, CTO, Lounea
- Dr. Marcus Brunner (moderator), ETSI ISG F5G Vice Chair, Chief Expert Standardization, Huawei
The 19th ETSI ISG F5G Plenary meeting was held in Sophia-Antipolis, France from August 27th to 30th 2024. As part of the Plenary meeting, an open session between ISG ZSM and ISG F5G was held. This is the first time these two ISGs have met together.
The ISG ZSM works on defining technical-agnostic end-to-end network and service management and operation framework and key technologies, which enables autonomous and future network. It is the goal of ISG F5G to apply the ZSM framework and its key enabling technologies, such as intent-based networking, Network Digital-Twin (NDT) and closed-loop automation, in the intelligent management and control of the F5G-A optical network.
Modern production facilities have to support on demand product customization to satisfy customer needs. One key technology to make this happen are Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs). These are mobile transport robots, which distribute raw materials and parts on the factory shop floor and potentially among different manufacturing halls and warehouses. The navigation of the AGVs on the factory shop floor or in outdoor areas is a computationally complex task requiring significant computing resources. Cloud-based AGV navigation enables cooperation and centralized information exchange between multiple robots and AGVs.
As the number and variation of AGVs within a production facility site increases, so does the complexity of their control, for guaranteeing a seamless and orchestrated operation.

Figure 1
In the ISG F5G F2F#19 plenary meeting held in Sophia-Antipolis, France from August 27th to 30th 2024, the creation of a new Work Item (WI) for F5G-A Use Cases Release 4 was agreed. The new work item is proposed by China Unicom and has eight supporting organizations including Orange, China Telecommunications, ZTE Corporation, CTTC, Huawei Technologies France, CAICT, POST Luxembourg and CICT. Mr. Yue Sun from China Unicom is the Rapporteur of this WI.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) together with the European Telecommunications Standards Institute – Industry Specification Group -Fifth Generation Fixed Network (ETSI ISG F5G), the Broadband Forum (BBF), and the China Communications Standards Association – Technical Committee 6 (CCSA TC6) organized the Fourth Joint ETSI ISG F5G, BBF, CCSA TC6 and ITU-T SG15 Workshop on "FTTR" (Fibre to the room), which took place 10 July 2024 from 8:00-12:00 (EDT)/14h00 to 18h00 (CEST) in Montreal, Canada.
The use case of on-premises fibre networks, such as FTTR, was firstly described in ETSI GR F5G 002 by the ISG F5G early in 2020. Since then, the related standards have been rapidly developed by several Standard Development Organisations (SDOs). The workshop intend was to offer the opportunity to continue the discussion on FTTR and other on-premises fibre networks for all the involved stakeholders, to reach a better common understanding of the use cases, the requirements, the deployment challenges, and the best practices. This workshop facilitates the development of an FTTR standard and the cooperation of multiple SDOs, as well as the system deployment by the network operators.

ETSI GR F5G 020, F5G Advanced Use Cases; Release 3 is publishing use cases to be enabled by the F5G Advanced (F5G-A) network. The use cases in that document include services and applications for residential customer, enterprises, vertical industries, network operation optimizations, and evolved fixed end-to-end infrastructure, which were not supported by the F5G network. Use cases will aim to introduce new technical requirements for the F5G Advance network along various characteristic dimensions. The use cases will be used as input to drive the technology development and standardization of new features for F5G Advanced based on the technical requirements derived from those use cases.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) together with the European Telecommunications Standards Institute – Industry Specification Group -Fifth Generation Fixed Network (ETSI ISG F5G), the Broadband Forum (BBF), and the China Communications Standards Association – Technical Committee 6 (CCSA TC6) are organizing the Fourth Joint ETSI ISG F5G, BBF, CCSA TC6 and ITU-T SG15 Workshop on "FTTR" (Fibre to the room), which will take place 10 July 2024 from 8:00‑12:00 (EDT)/14h00 to 18h00 (CEST) in Montreal, Canada. This is an in-person event with remote participation.

On May 28th ~ 31st 2024, the 18th ETSI ISG F5G Plenary meeting was held in Luxembourg, hosted by POST Luxembourg. Significant progress was made during the meeting.

The development of the proof of concept "Visual inspection for automatic quality assessment PoC" started in May 2023 and was successfully finished in November 2023. Several goals have been set:
- implementation of a PON based industrial Edge/Cloud-based; and
- visual inspection for quality assessment of products and to demonstrate a low-latency ML‑based video processing-pipeline for end-to-end manufacturing control loop.
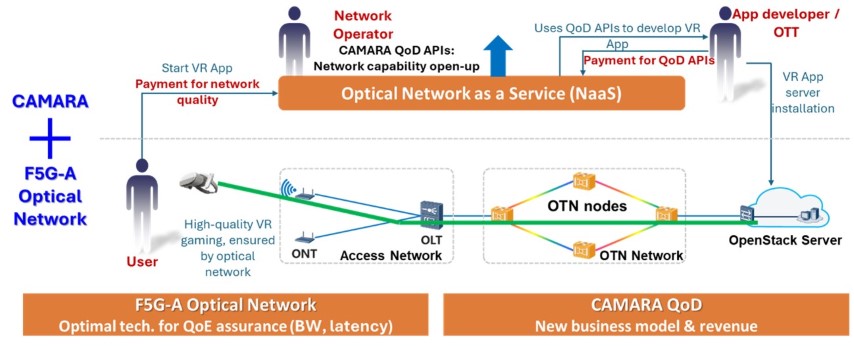
At the Mobile World Congress 2024, the Centre Tecnològic de Telecomunicacions de Catalunya (CTTC) and Huawei Technologies introduced a groundbreaking Proof of Concept (PoC) that underscores the capabilities of the ETSI Industrial Specification Group (ISG) Fifth Generation Fixed Network (F5G). This demonstration exemplified a significant leap in Fixed 5G technology, using a Virtual Reality (VR) Gaming Service for Remote Players as a practical application of the F5G Advanced (F5G-A) architecture. The F5G-A architecture exploits the optical network capacities to provide high quality transmission with ultra-low end-to-end latency, high bandwidth guarantees, and minimized jitter to ensure the Quality of Experience (QoE) for cloud-based services. This architecture promises to reshape a myriad of high-demand digital services, offering unparalleled connectivity and intelligent End-to-End (E2E) service management.
On February 20th ~ 23rd 2024, the ETSI ISG F5G #17th Plenary meeting was held in Sophia Antipolis, France. This is the first plenary meeting of the ISG F5G third term.
In the meeting, the election of F5G Chair and Vice-Chairs for the third term was held. Dr. Olivier Ferveur from POST Luxembourg was appointed the ISG F5G Chair effective immediately. Dr. Marcus Brunner from Huawei Technologies (UK) Co., Ltd. and Dr. Jialiang Jin from China Telecom were appointed the Vice-Chairs (the mandates of F5G Vice-Chairs will start on 17th April 2024).
On January 23rd 2024, an ETSI webinar "How can all-optical networks contribute to carbon transition?", was presented by ETSI ISG F5G, to disseminate the ETSI White Paper "All-optical network facilitates the Carbon Shift" published in November 2023.

This White Paper was developed by ISG F5G to provides an overview of an all-optical network and the recent developments in optical technologies, and highlights the role of all-optical networks as a key ICT enabler to meet the UN sustainability goals.
In this webinar, there were four speakers, that included the co-editors / contributors of the White Paper, who shared their viewpoints on green all-optical networks:
- Mr. Jean-Luc Lemmens, Co-Editor, CEO IDATE
- Dr. Olivier Ferveur, F5G Acting-Chair ISG F5G, Post Luxembourg
- Dr. Xiangkun Man, Co-Editor, China Unicom
- Dr. Marcus Brunner, Liaison Officer in ISG F5G, Huawei
On November 30th 2023, an important ETSI ISG F5G Group Report was released. The title of the report is “Fifth Generation Fixed Network (F5G); F5G Advanced Generation Definition” [ETSI GR F5G 021]. This is the first report for the F5G Advanced generation in Release 3. The publication of the ETSI GR F5G 021 is a significant milestone for ISG F5G, which is steadily evolving from F5G to F5G Advanced.
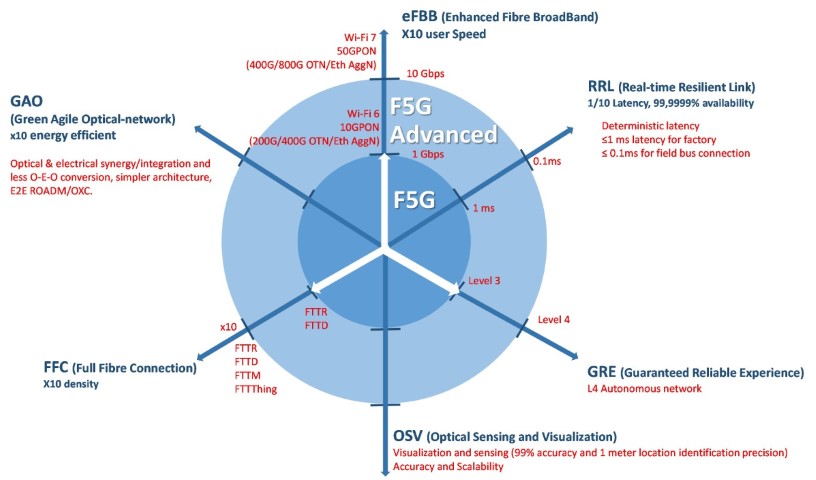
Six dimensions of F5G Advanced with enabling technologies characteristics
